

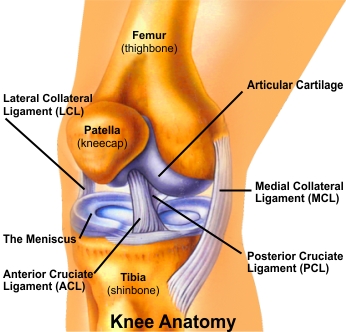
Your knee is a hinge joint where the end of the thigh bone (femur) meets the beginning of the large bone in your lower leg (tibia). A healthy knee has smooth cartilage that covers the ends of the femur and tibia. The smooth cartilage lets the surfaces of the two bones glide smoothly as you bend your knee. The muscles and ligaments around the knee joint support your weight and help move the joint smoothly so you can walk without pain.
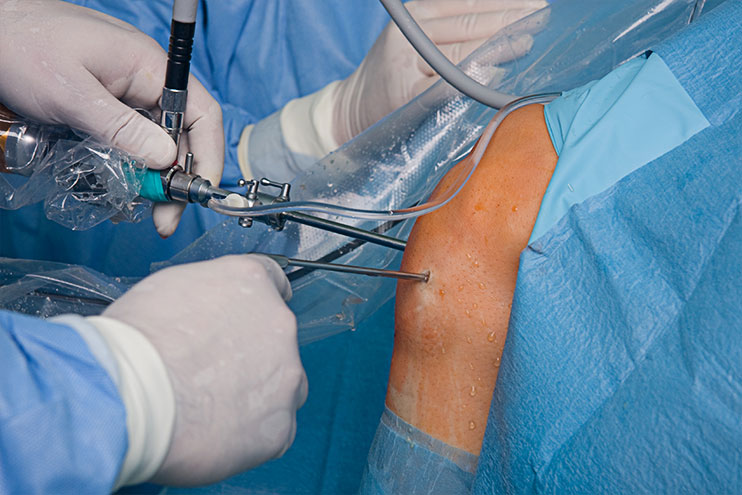
Knee Arthroscopy is a procedure that allows Dr. (Prof.) Anil Arora to look inside of your knee using an arthroscope (a slender scope that contains a lens and a light source). This enables him to obtain a clear view of the knee, diagnose, and treat knee conditions and injuries. Small incisions are made around the knee to insert the arthroscope, irrigating tool, and reparative instruments. The images are then projected on a television screen in the operating room, so that the Dr. Arora has an enhanced view of the knee and tissues.
Tradional knee surgery techniques included a large incision with an open procedure, and a lengthy hospitalization. With arthroscopy, the procedure is minimally invasive and the recovery is typically rapid. The patients either are hospitalized for one day or return home the same day.
Signs that you may be a candidate for this procedure include swelling, persistent pain, catching, giving-way, and loss of confidence in your knee. On the basis of physical examination, x-rays and MRIs your Dr. (Prof.) Anil Arora will make an evaluation to determine whether you could benefit from arthroscopy.
Dr. Arora makes a small incision in the skin and inserts the arthroscope. Usually 2 to 3 incisions, called portals, are necessary in order to examine the inside of the joint. A sterile fluid is introduced into the knee joint to wash it out and expand it, making room for the arthroscope and surgical instruments.
A surgical instrument is used to probe various parts within the joint to determine the quality of the tissue and extent of the problem. If surgery is indicated, it is performed with specially designed manual or power-driven instruments that are inserted into the joint through the portals.
The image below shows arthroscopy of the knee.
After arthroscopic surgery is over, the portals are closed with sterile surgical tape and covered with a layer of gauze and crêpe bandage. The patient is then moved from the operating room to a recovery room where a nurse will monitor temperature, blood pressure and heartbeat.
Before being discharged, usually several hours after your operation, you will be seen by your anaesthetist and Dr. (Prof.) Anil Arora and one of his physiotherapists. You will learn how to care for your arthroscopic portals, what activities you should avoid, and what exercises you should do to aid your recovery.
At a follow-up visit (usually 10 to 14 days after the operation) Dr. Arora will inspect arthroscopic portals, remove the skin closure and discuss the operative findings and further rehabilitation programme.

Your knee is a hinge joint where the end of the thigh bone (femur) meets the beginning of the large bone in your lower leg (tibia). A healthy knee has smooth cartilage that covers the ends of the femur and tibia. The smooth cartilage lets the surfaces of the two bones glide smoothly as you bend your knee. The muscles and ligaments around the knee joint support your weight and help move the joint smoothly so you can walk without pain.
The Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) is located in the center of the knee joint where it runs from the backside of the femur (thighbone) to connect to the front of the tibia (shinbone). The ligament runs through a special notch in the femur (thighbone) called the intercondylar notch and attaches to a special area of the tibia (shinbone) called the tibial spine.
It is probably the most commonly injured ligament of the knee. A sports injury, a fall from bike and/or traffic accident are the usual causes. The injury is followed by swelling and pain in the knee joint. Gradually pain and swelling subside, but "Unstable Knee" develops which means you will feel that your knee will give way. You lose confidence in day to day activities, more so in high demand activities. You will have falling tendency or you may actually fall, while suddenly turning during a walk, catching a bus, jumping out of a car etc. It may stop you doing your normal work and sports.
The ACL is the main controller of how far forward the tibia moves under the femur. If the tibia moves too far, the ACL can rupture. The ACL is also the first ligament that becomes tight when the knee is straightened. If the knee is forced past this point, or hyper extended, the ACL can also be torn.
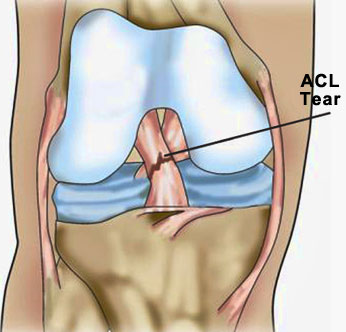
The location of the ACL in the knee joint makes it unlikely to heal when injured. Thus, reconstruction is the procedure of choice for restoring normal knee stability and avoiding further injury to the meniscus and/or cartilage. Most surgeons now favour reconstruction of the ACL using a graft from the patient's own leg to replace the torn ACL. There are two grafts commonly used to repair a torn ACL. One is a strip of the patellar tendon below the kneecap. The other is the hamstring tendongraft.
This injury has received a great deal of attention from orthopedic surgeons over the past 15 years, and very successful operations to reconstruct the torn ACL have been invented.
Your surgery will be performed by Dr. (Prof.) Anil Arora using an arthroscope (keyhole), a small fiber-optic video camera that is used to see and operate inside the joint. Only small incisions (portals) will be made during arthroscopy for this procedure. The surgery doesn't require Dr. (Prof.) Anil Arora to open the knee joint.
The following video animation displays how the ACL is reconstructed.
The surgery is performed on an outpatient basis, and many patients go home on the same day as the surgery.
Patients take part in formal physiotherapy after ACL reconstruction. The first few physiotherapy sessions are designed to help control the pain and swelling from the surgery. The goal is to help them regain full knee extension as soon as possible.
As the rehabilitation programme evolves, more challenging exercises are chosen to safely advance the knee's strength and function. Specialized balance exercises are used to help the muscles respond quickly and without thinking. This part of treatment is called neuromuscular training which includes exercises to improve balance, joint control, muscle strength and power, and agility. Agility makes it possible to change directions quickly, go faster or slower, and improve starting and stopping. These are important skills for walking, running, and jumping, and especially for sports performance.
When the patient gets full knee movement, and his/her strength and muscle control are improving, they'll be able to gradually go back to their work and sport activities. Ideally, the patients will be able to resume their previous lifestyle activities. However, athletes are usually advised to wait at least six months before returning to their sports (depending on the nature of the sport - contact sports usually take a year to get back to and two years for them to get back to the level they played the sport prior to the injury).